Evolving a soft robot
Let’s see who is the fastest soft robot :). GitHub Link: https://github.com/JiaweiChenC/Robot-evolving
Goal
Generate a set of soft robots from scratch, evolve them with EA, then find the fastest soft robot.
What we need
- A physical simulator
- Basic computer graphics to rendering the soft robot.(build with OpenGL)
- A effective EA strategy(how to mutate and crossover).
- Some technique to make it faster.(C++ & CUDA)
Physical simulator
Basic primitives
Masses:
- Point masses(no volume)
- Have position, velocity and acceleration
Springs:
- Massless
- Connect two masses
- Have a rest length and stiffness
- Apply restoring forces on the masses
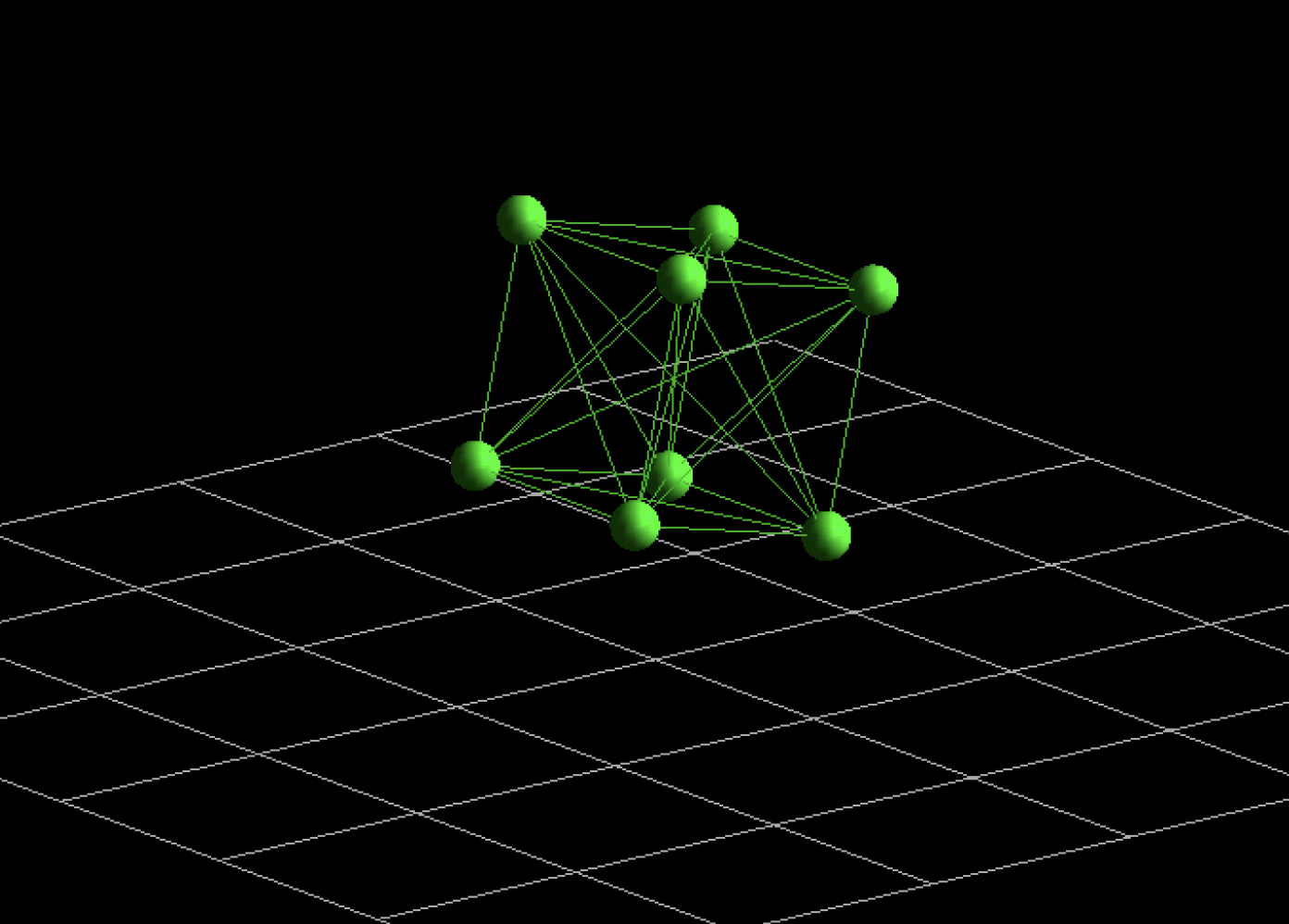
Figure 1: Bouncing Cube
Basic simulator
- Choose a discrete time step dt
- At each time step:
- T = T + dt
- Interaction step:
- Compute and tally all the forces acting on each mass from springs connected it
- Integration step: h - Update position and velocity of each atom using Newton’s laws of motion F=ma.
Combine together
Combine a lot of cubes together, we can get a physical engine!
Figure 1: Bouncing Cubes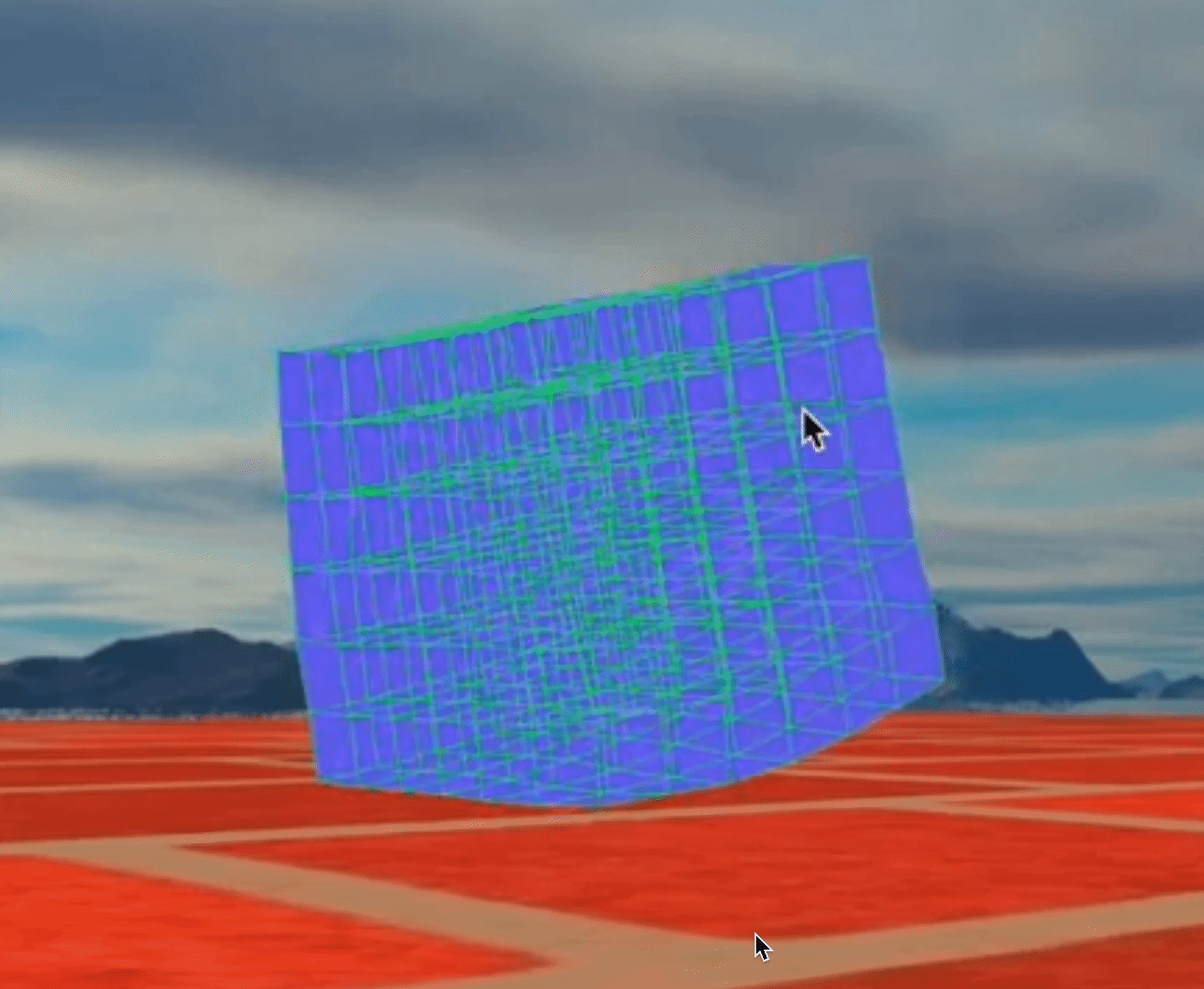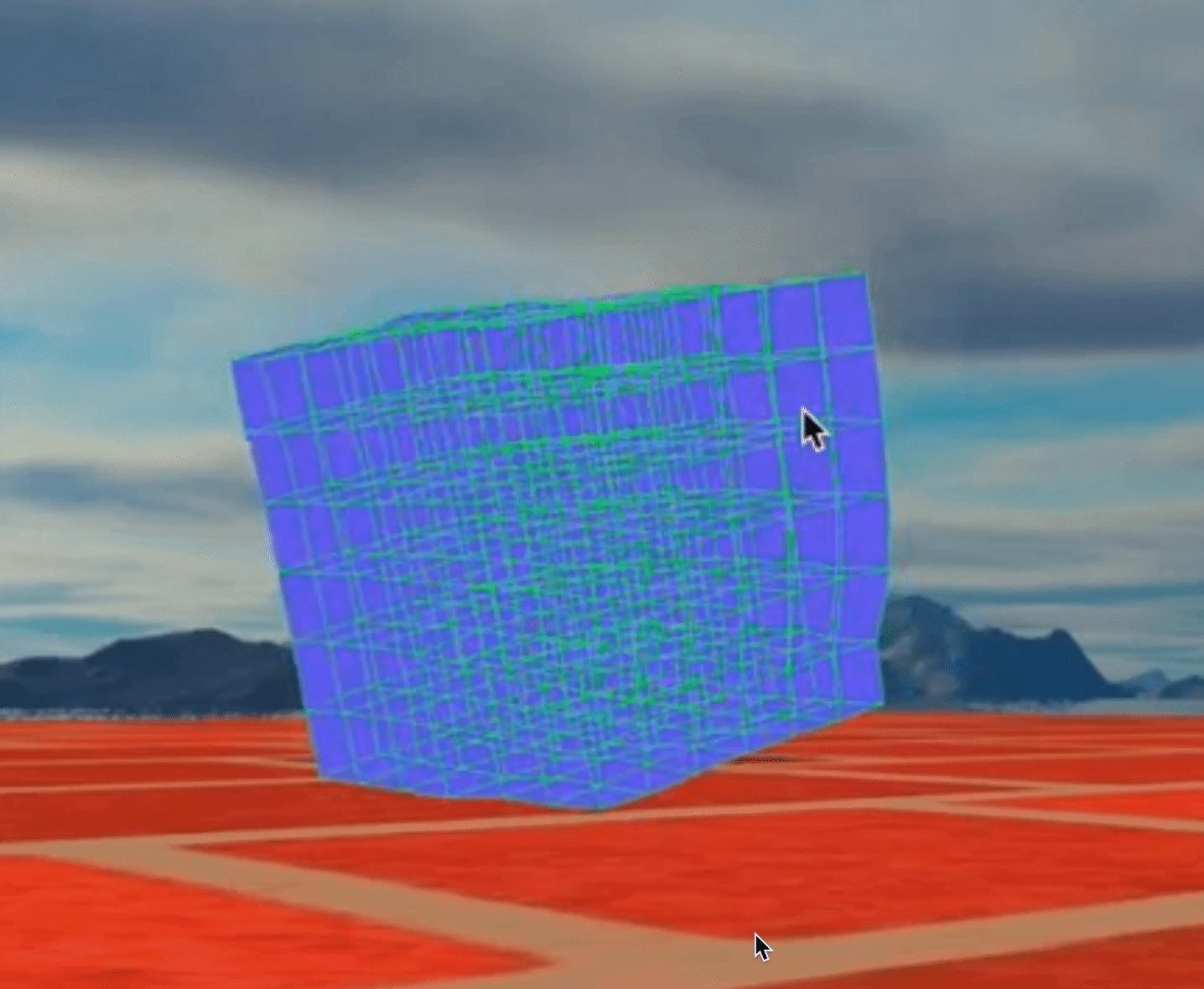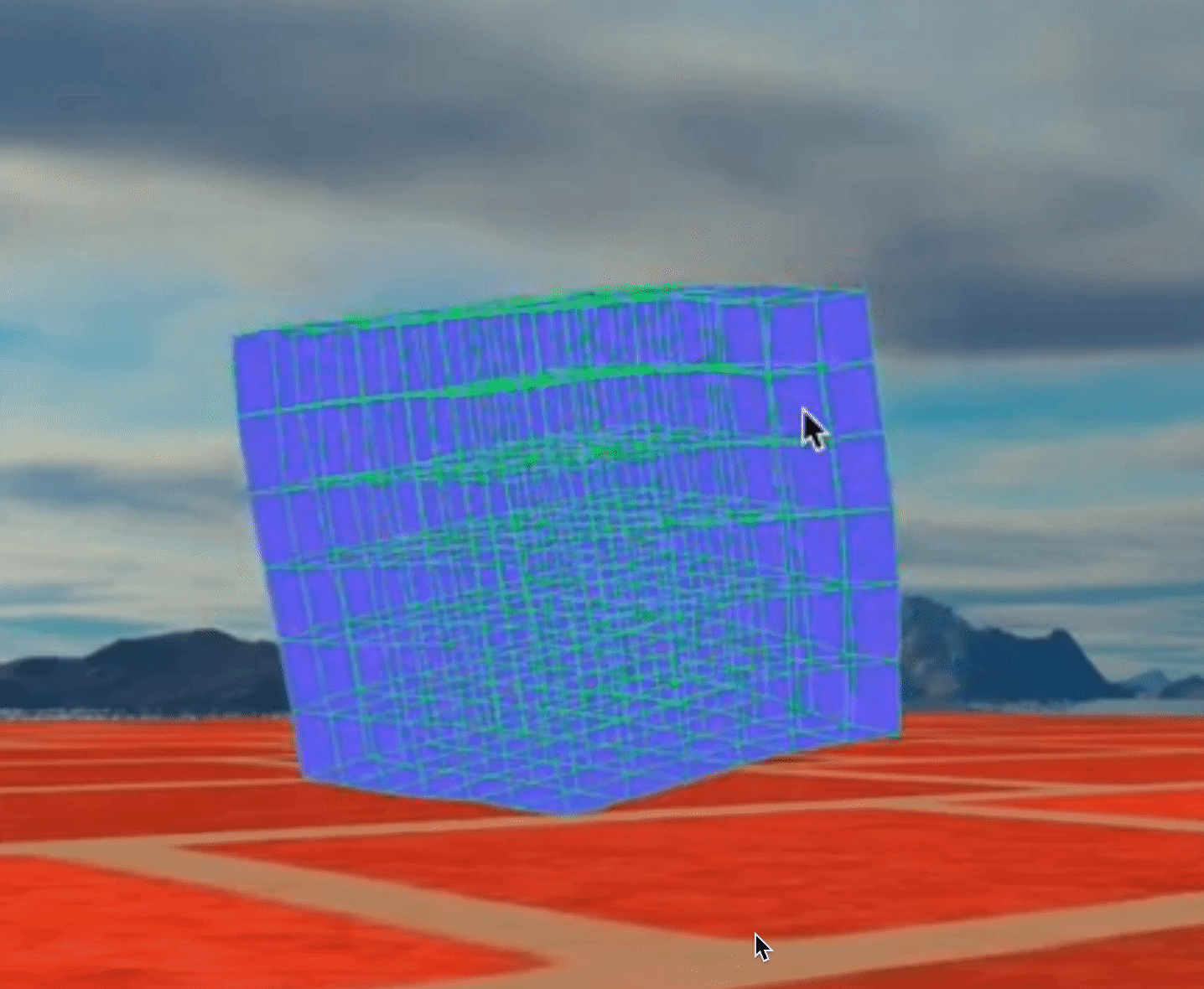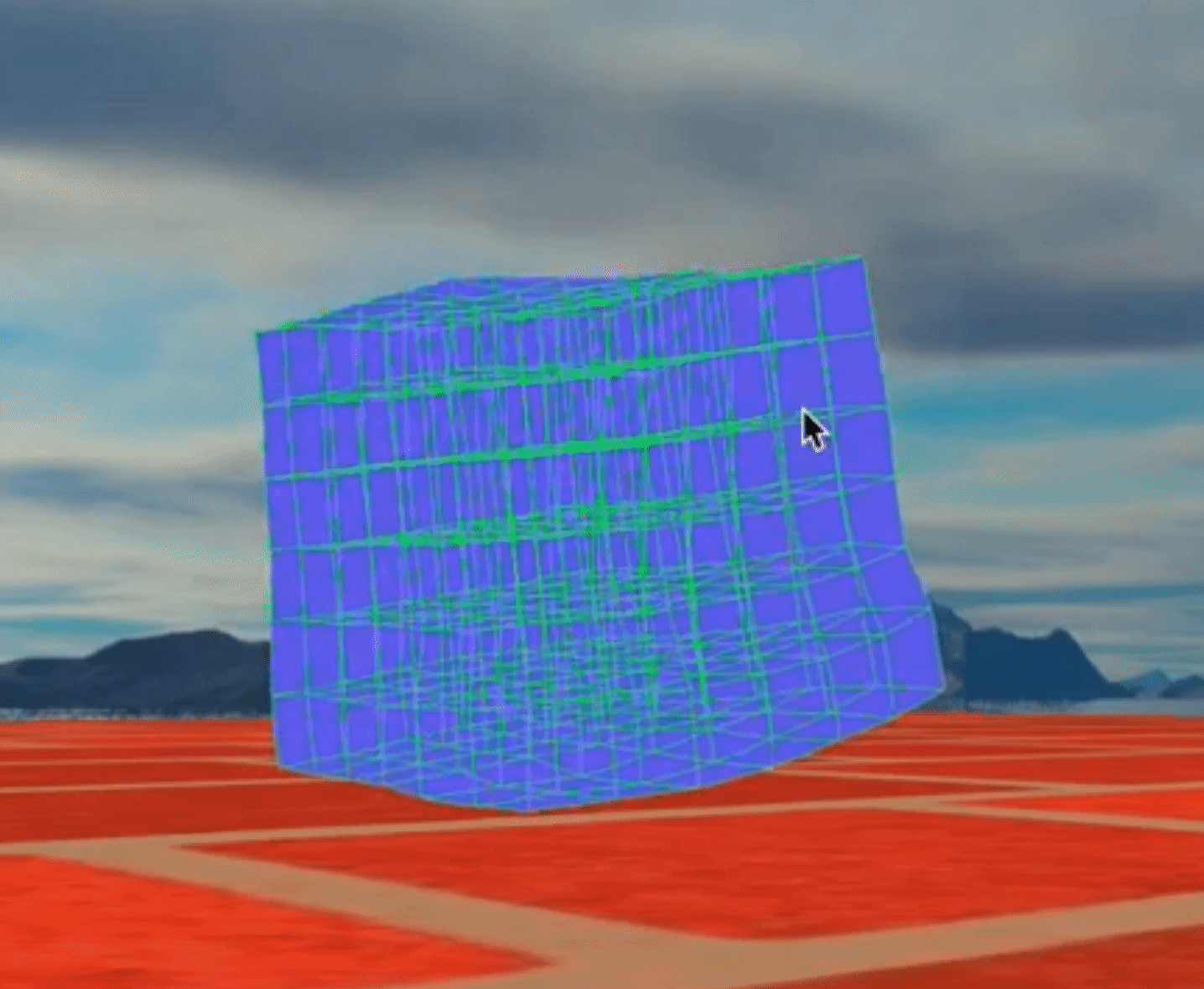
Evolutionary Algorithm
In computational intelligence (CI), an evolutionary algorithm (EA) is a subset of evolutionary computation,a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses mechanisms inspired by biological evolution, such as reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection. Candidate solutions to the optimization problem play the role of individuals in a population, and the fitness function determines the quality of the solutions (see also loss function). Evolution of the population then takes place after the repeated application of the above operators.
Competition
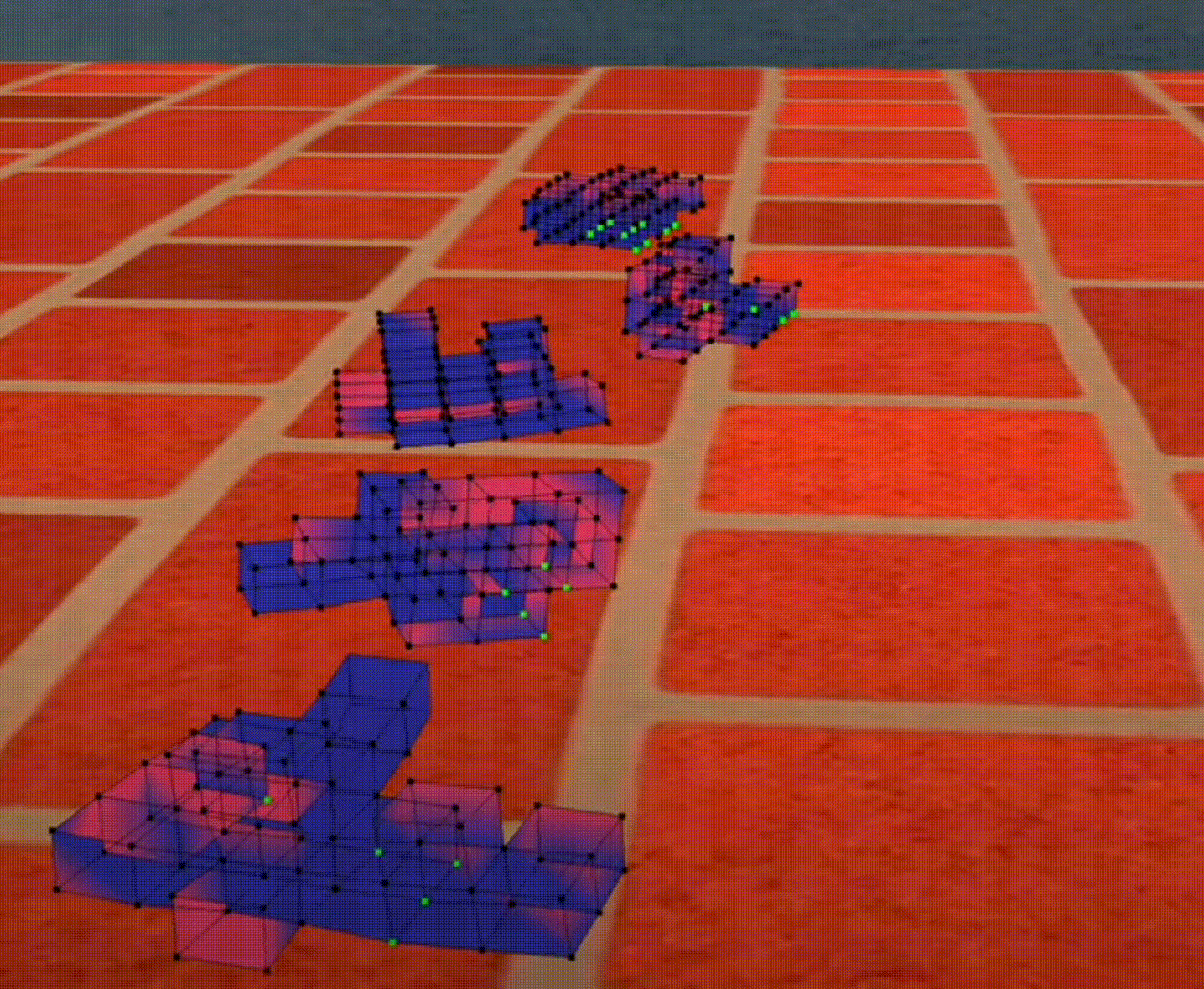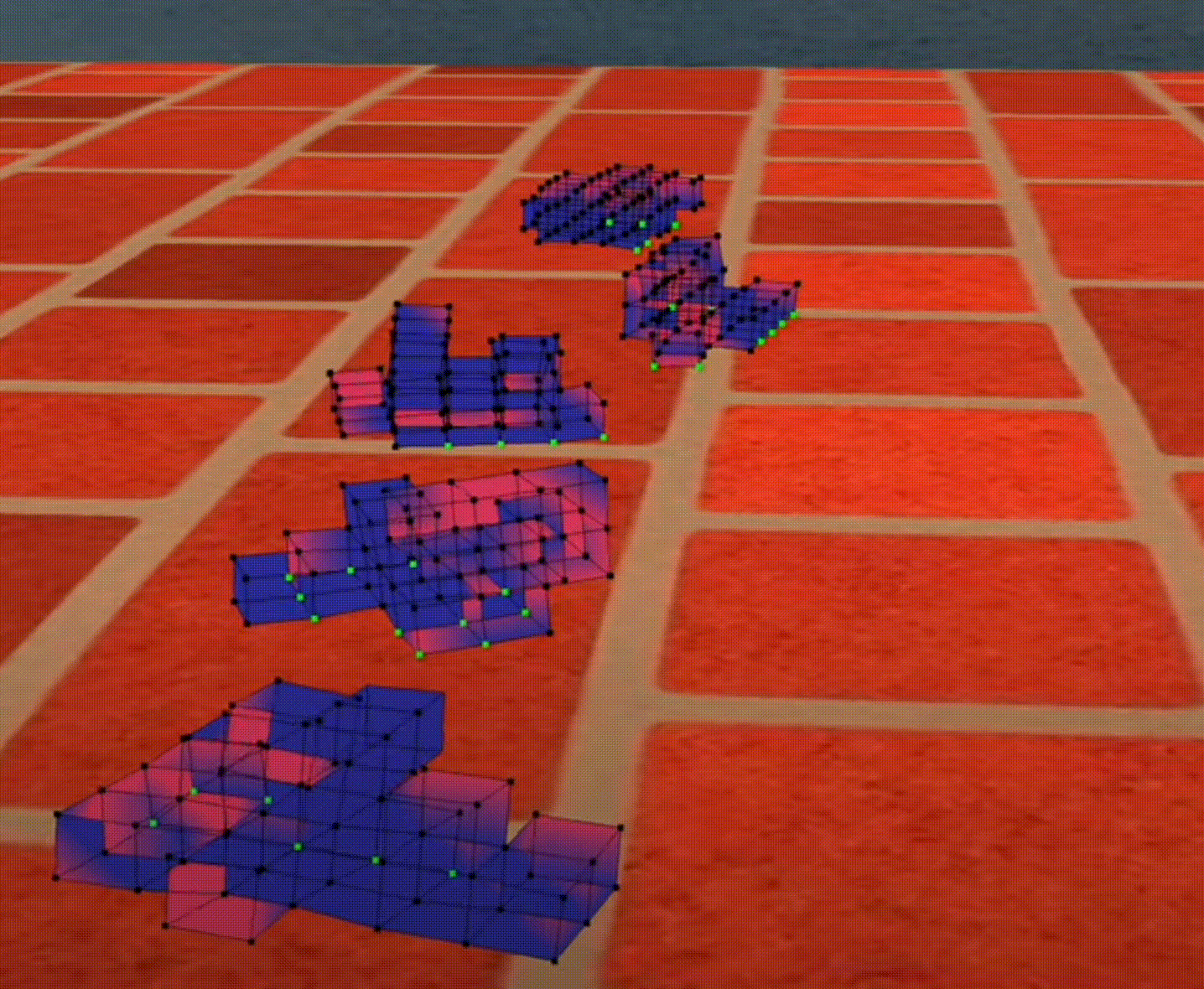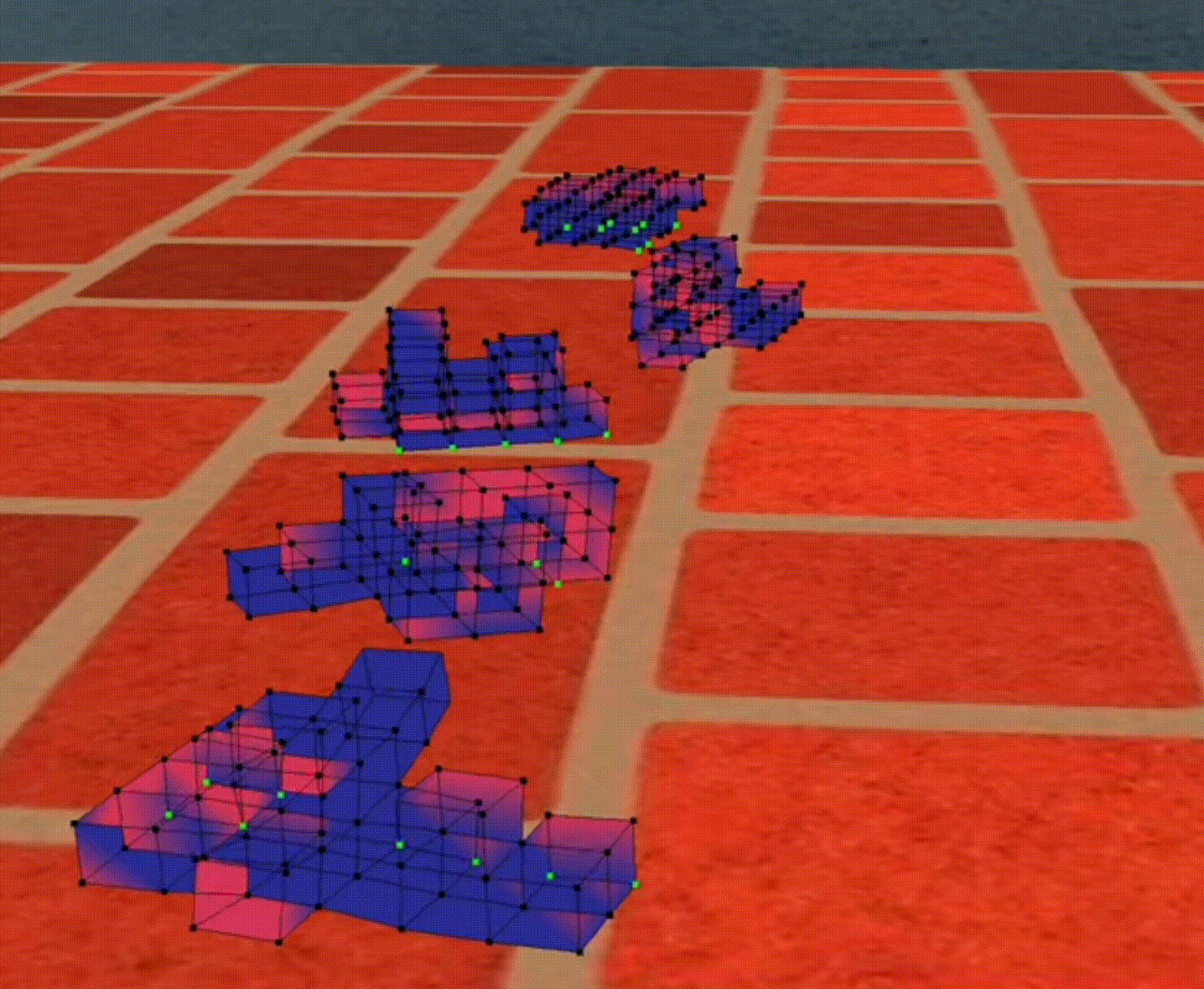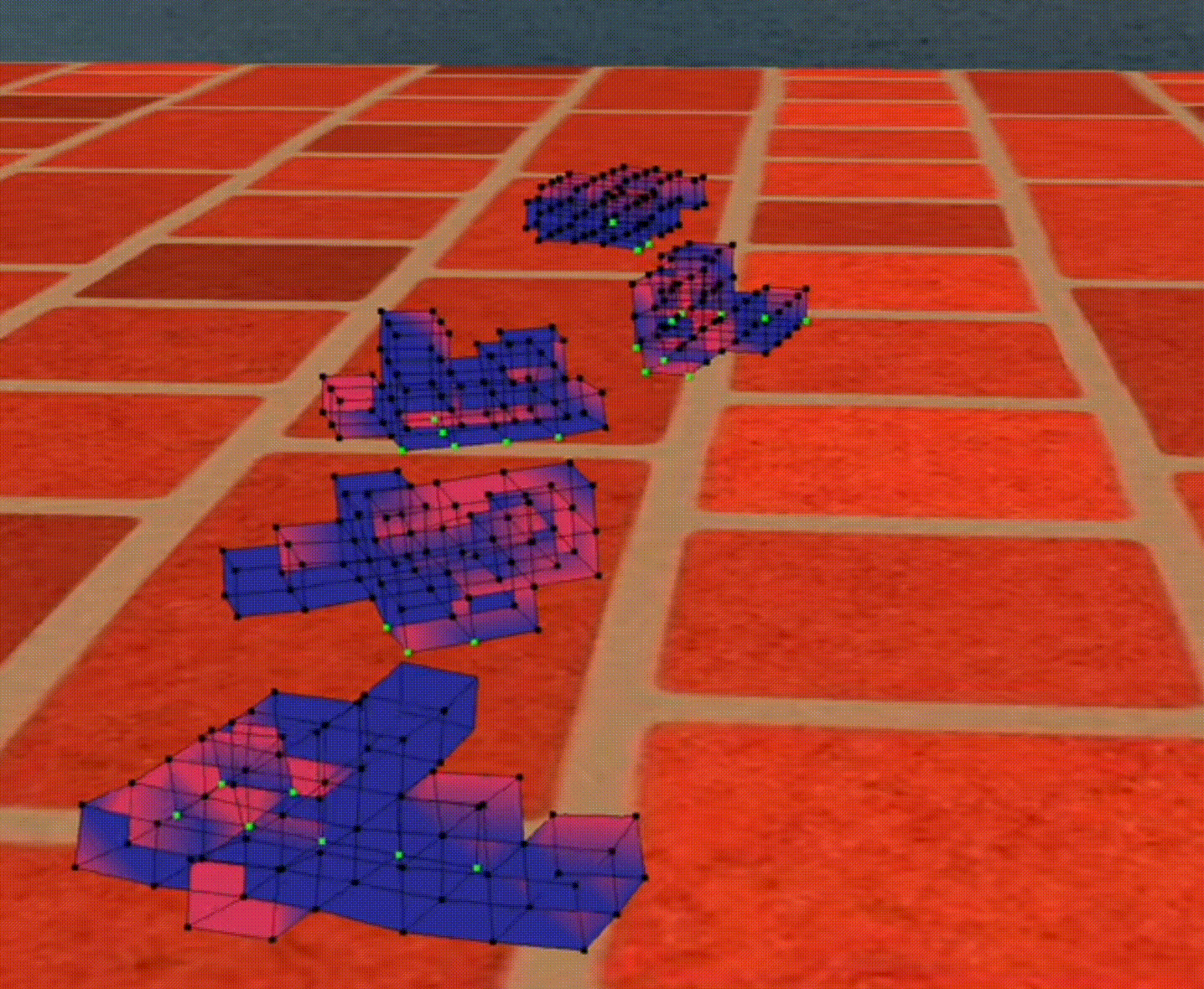
Figure 1: Bouncing Cubes
- At the beginning, all the robots were just “trembling
- After some time the robots can move a little bit
- After a lot of generations, the robots developed their strategy to move “FAST”
a FAST robot
Robots will use very interesting strategy to be faster, e.g., this robot have a big head so it can fall on the ground quickly and move faster than others.
Figure 1: A fast robot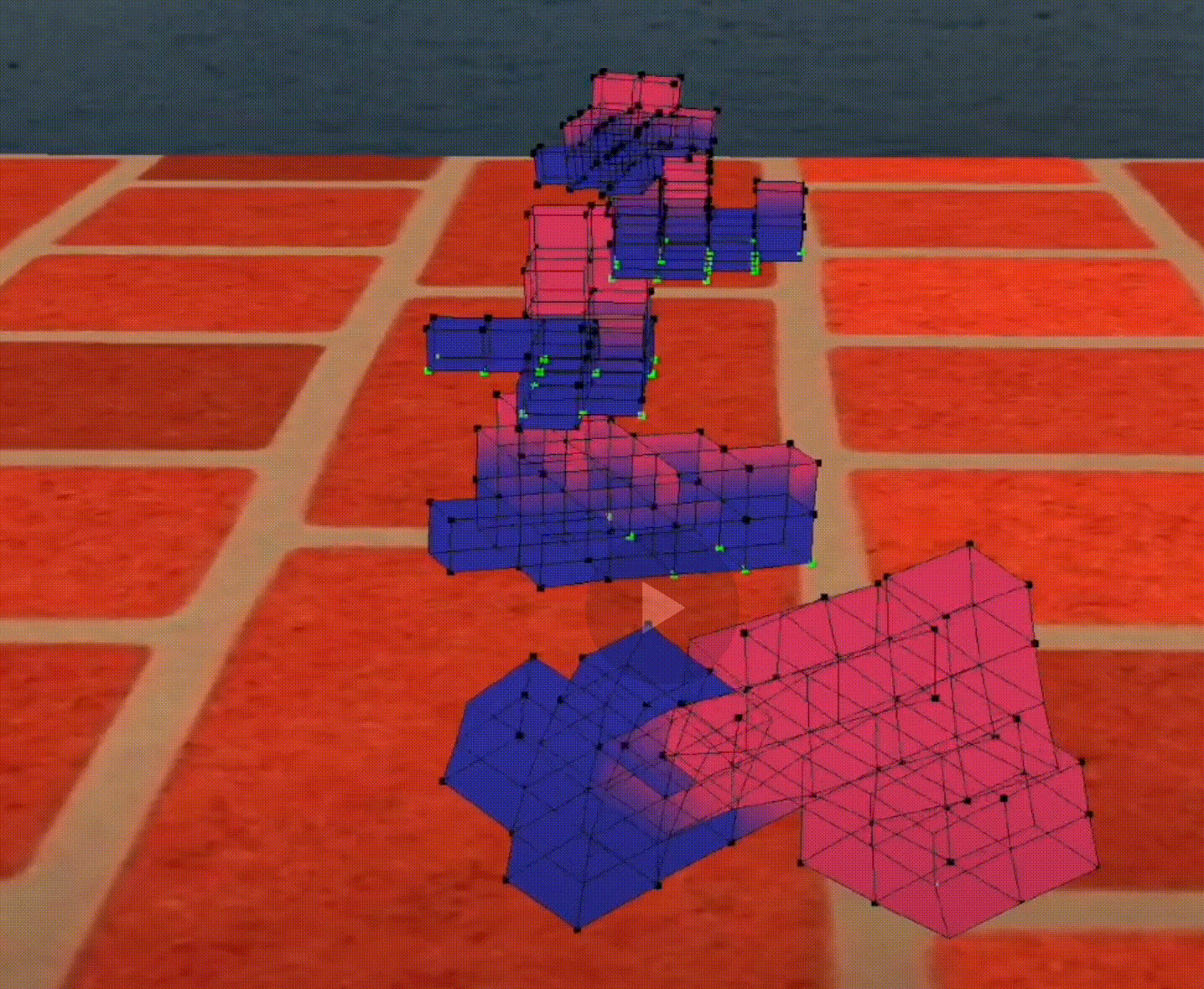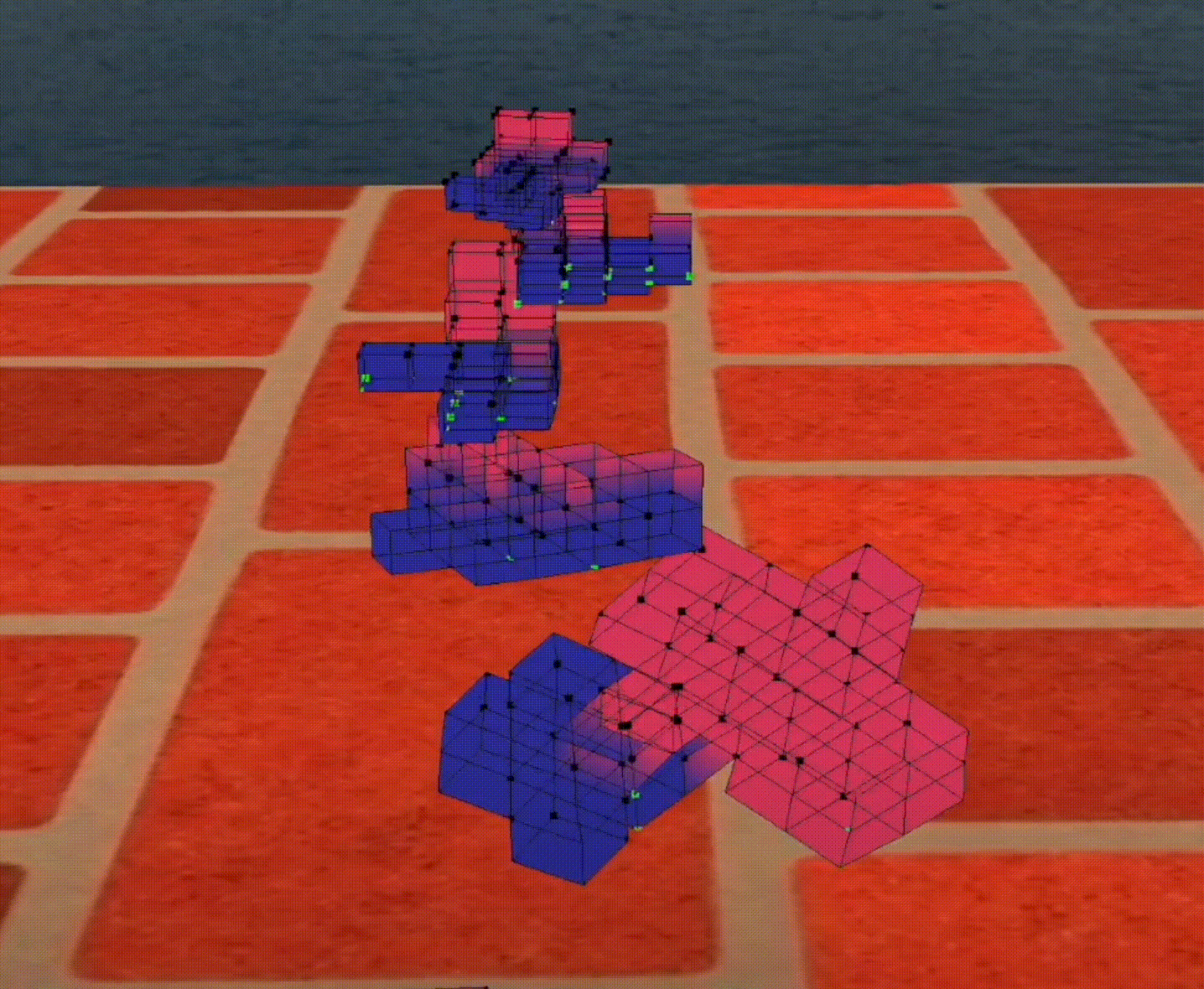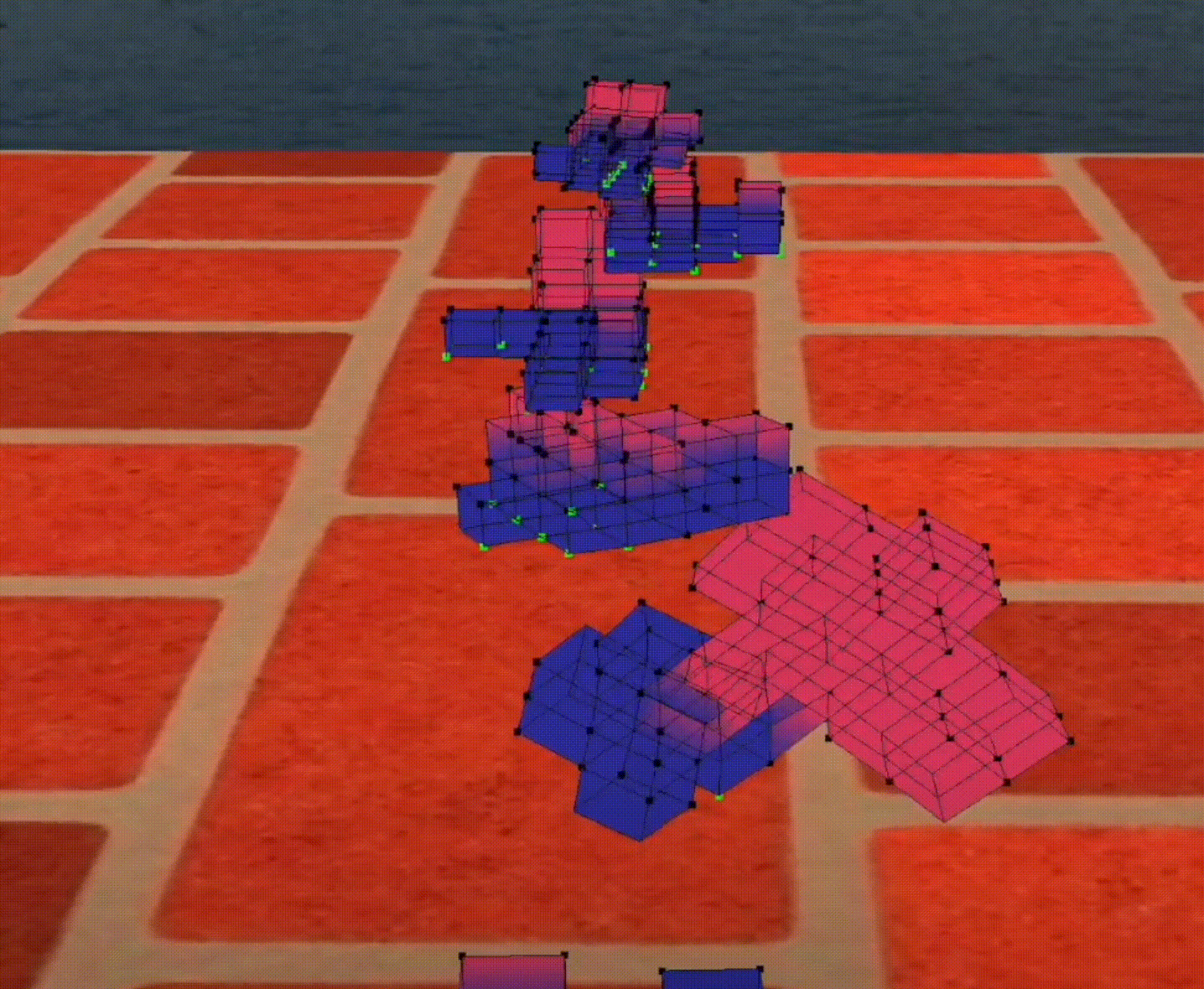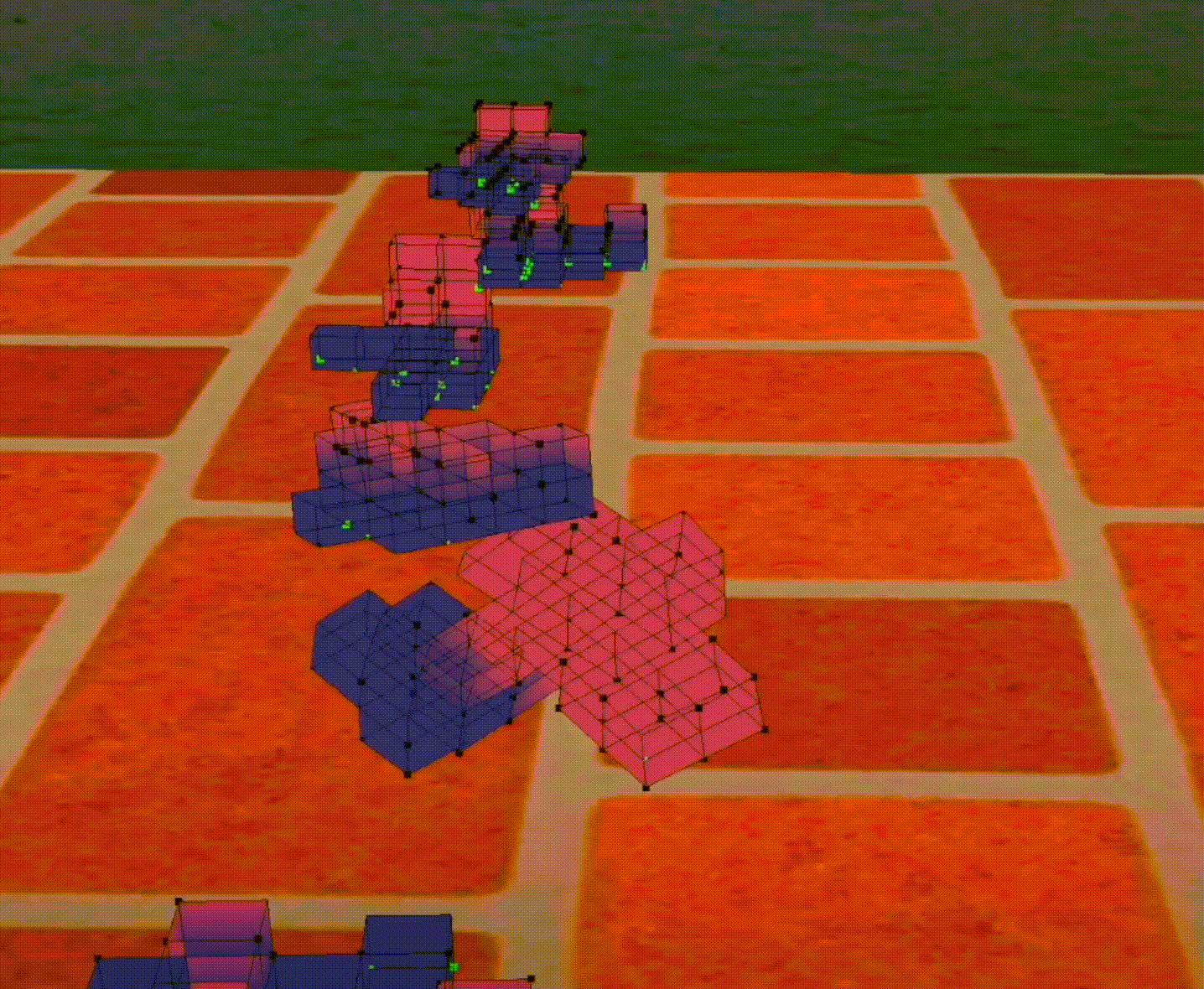
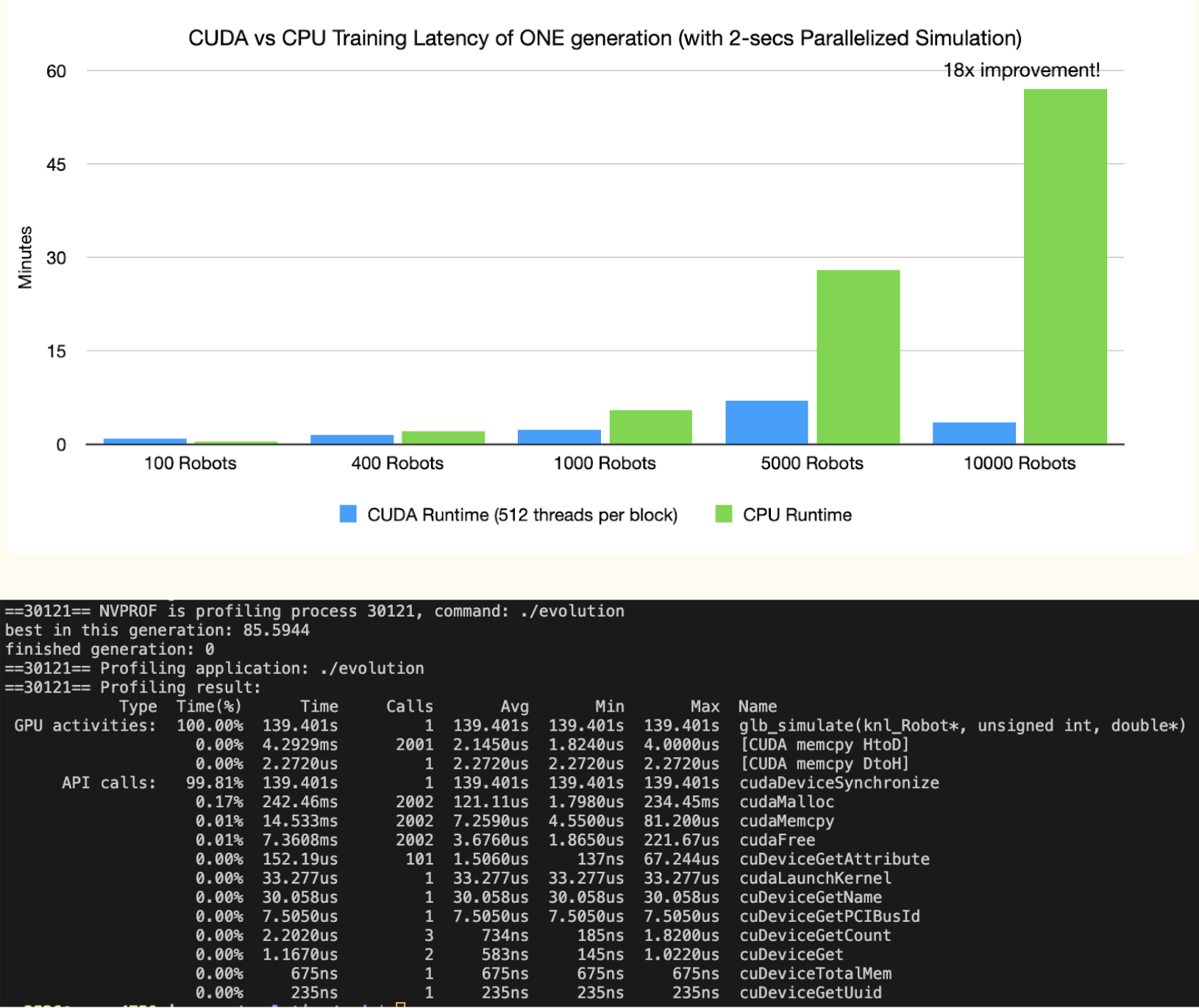
CUDA
Another interesting part is using CUDA to accelerate the process.
Figure 1: Using CUDA